Introduction
Gastroparesis is a condition where the stomach’s normal movement is impaired, causing slow food emptying. It can occur due to weakened nerves and muscles responsible for stomach contractions. While it’s often linked to diabetes, it can affect anyone, sometimes masquerading as ulcers or heartburn.
Causes of Gastroparesis 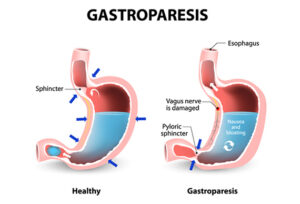
Several factors contribute to gastroparesis, including nerve damage, especially to the vagus nerve, often caused by diabetes. Other triggers can be viral infections, certain medications like narcotics and antidepressants, and connective tissue disorders affecting various organs.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of gastroparesis include heartburn, nausea, vomiting undigested food, early fullness, bloating, stomach discomfort, appetite loss, weight loss, and blood sugar control issues. Diagnosis involves a thorough evaluation of symptoms, medical history, and physical exams. Blood tests, including glucose tests, may be necessary. Specialized tests like a gastric emptying study and a smart pill study may also be used to diagnose.
Management and Treatment
While gastroparesis has no cure, it can be managed effectively. For diabetics, maintaining stable blood sugar levels can help prevent it. Medications like Reglan, Erythromycin, and antiemetics may be prescribed to improve stomach contractions and alleviate nausea. Surgical options like gastric bypass or gastric stimulator implantation are considered in cases where medications don’t work. A non-surgical option, per-oral pyloromyotomy, can also help by cutting the pylorus valve to aid food passage.
Dietary Modifications
Making dietary adjustments is vital in managing gastroparesis. Eating smaller, more frequent meals (at least six a day) can aid digestion by reducing stomach volume.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gastroparesis involves delayed stomach emptying and disrupted motility. While there’s no cure, it can be managed through medications, surgery, lifestyle changes, and innovative treatments like per-oral pyloromyotomy. Early diagnosis and management are crucial for a better quality of life.